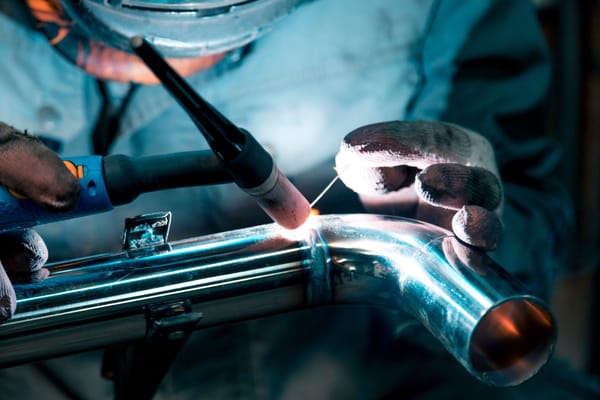
What is Metal Inert Gas (MIG) Welding?
Metal Inert Gas (MIG) welding, also known as Gas Metal Arc Welding (GMAW), is a welding process where a continuous solid wire electrode is fed through a welding gun and into the weld pool, joining two base materials.
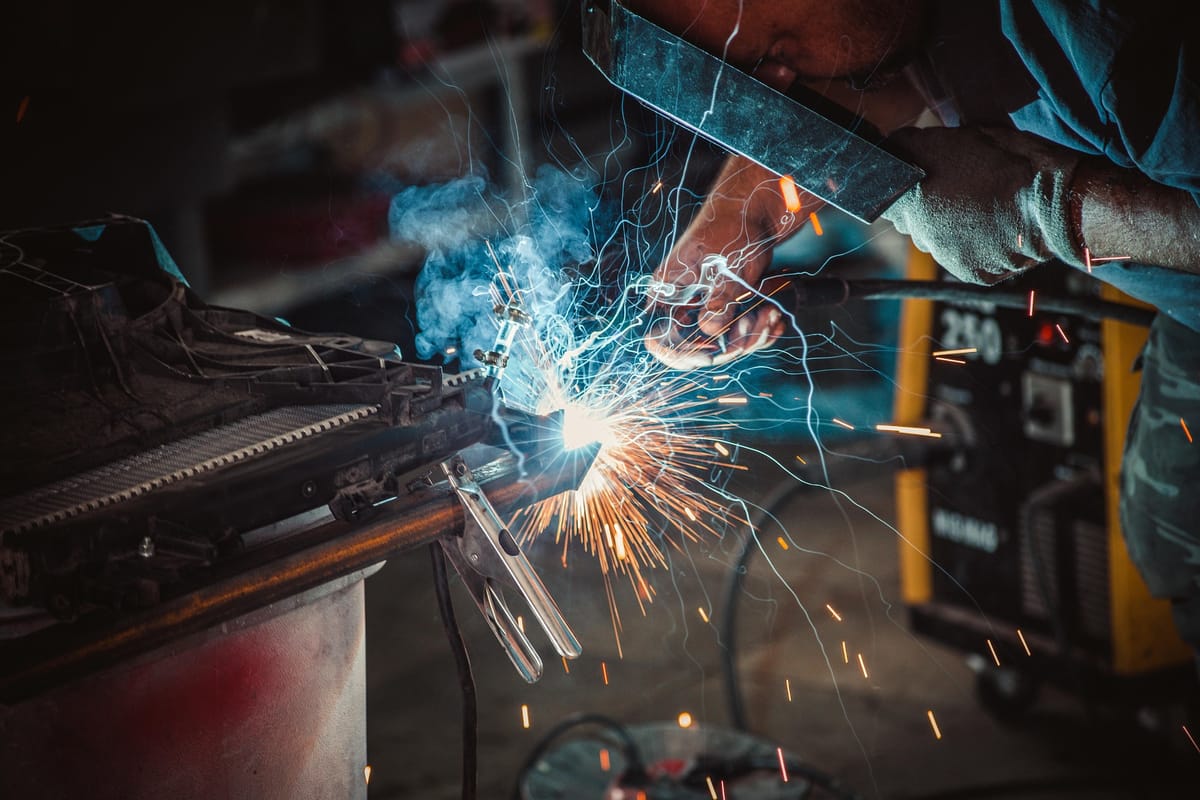

Metal Inert Gas (MIG) welding, also known as Gas Metal Arc Welding (GMAW), is a welding process where a continuous solid wire electrode is fed through a welding gun and into the weld pool, joining two base materials. The weld area is protected by a shielding gas that prevents contamination from atmospheric gases.
Brief History of MIG Welding
MIG welding was first developed in the 1940s for welding aluminum and non-ferrous metals. Over time, advancements in technology made it suitable for steel and other materials, making it popular in various industries today.
How MIG Welding Works
Basic Components of MIG Welding
- Welding Machine: Provides the electric current.
- Wire Electrode: Continuously feeds into the weld.
- Shielding Gas: Protects the weld from contamination.
- Welding Gun: Directs the electrode and gas flow.
The Welding Process Explained
The welding gun feeds the wire electrode into the weld joint while releasing shielding gas. An electric arc melts both the wire and the base material, forming a strong weld.
Key Equipment in MIG Welding
Welding Machine
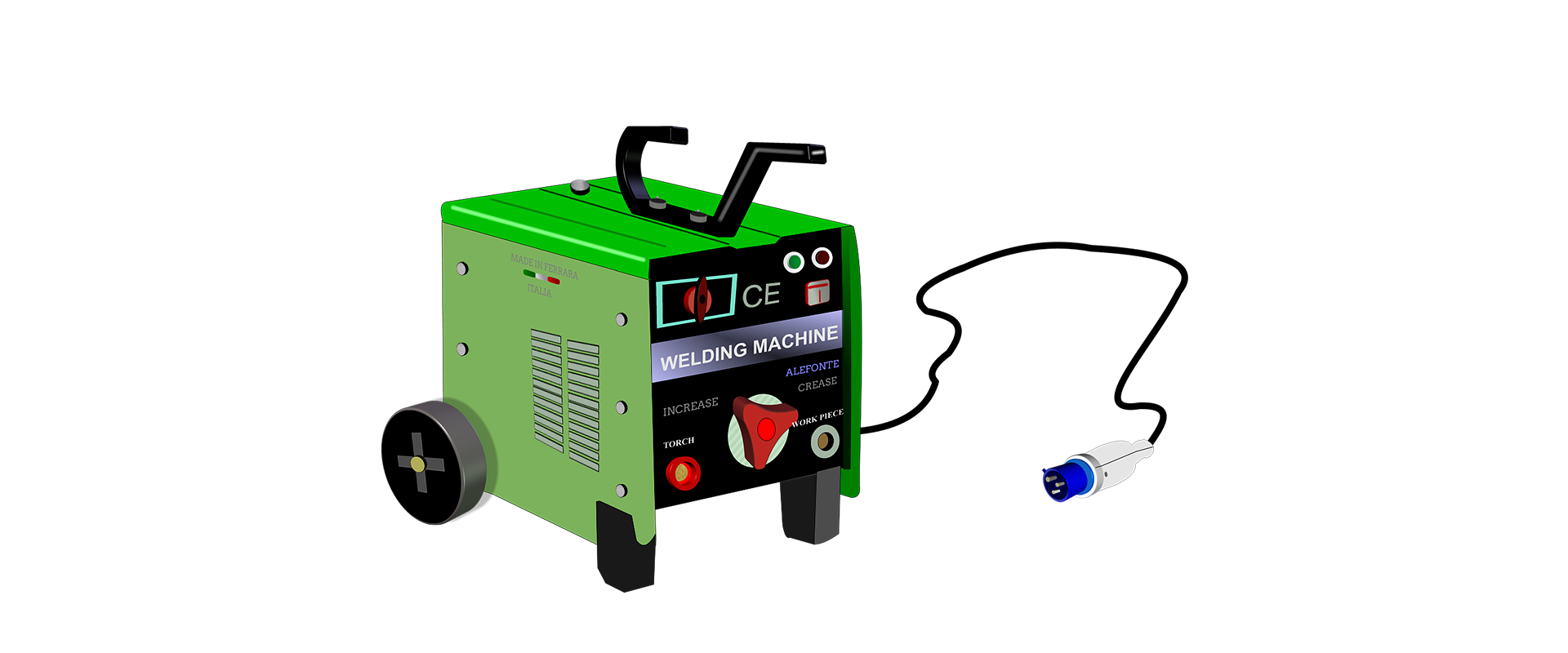

Controls voltage and current, critical for welding quality.
Electrode Wire
Common materials include mild steel, stainless steel, and aluminum wires.
Shielding Gas
Inert or semi-inert gases like argon, CO₂, or a mix protect the weld pool.
Types of Shielding Gases
Argon
Ideal for welding aluminum and non-ferrous metals, producing a stable arc.
CO₂
Common for welding steel, offering deeper penetration but more spatter.
Argon-CO₂ Mix
Combines the benefits of both gases for cleaner and more efficient welds.
Advantages of MIG Welding
Ease of Use
MIG welding is user-friendly, making it great for beginners.
Versatility
Suitable for various metals like steel, aluminum, and stainless steel.
High Welding Speed
Faster than other methods, increasing productivity.
Disadvantages of MIG Welding
Limited Outdoor Use
Wind can blow away the shielding gas, causing weld defects.
Equipment Cost
Initial setup is more expensive than other welding methods.
MIG Welding vs. Other Methods
MIG vs. TIG Welding
MIG is faster and easier, while TIG offers more precision.
MIG vs. Stick Welding
MIG produces cleaner welds but is less effective outdoors.
Common Applications
Automotive Industry
Used for car body repairs and manufacturing.
Construction
Ideal for structural steelwork and frameworks.
Metal Fabrication
Perfect for creating metal parts and products.
Safety Precautions
Protective Gear
Wear welding helmets, gloves, and flame-resistant clothing.
Safe Workspace Setup
Ensure proper ventilation and a clutter-free area.
Tips for Beginners
Selecting the Right Settings
Adjust voltage and wire speed based on material thickness.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
Avoid poor gas flow and incorrect electrode angles.
Maintenance of MIG Equipment
Cleaning the Nozzle
Regularly remove spatter to maintain gas flow.
Checking the Wire Feed
Ensure smooth wire feeding to prevent welding defects.
Advanced MIG Techniques
Spray Transfer
A high-heat method producing smooth, strong welds.
Pulse MIG Welding
Alternates between high and low currents for better control.
Environmental Impact
Fume Emissions
Proper ventilation reduces exposure to harmful fumes.
Energy Consumption
MIG welding consumes more power than some alternatives.
Future of MIG Welding
Technological Innovations
Developments in automation and robotics are enhancing welding efficiency.
Automation in MIG Welding
Robotic MIG welders are now common in mass production.
Conclusion
MIG welding stands out for its versatility, speed, and ease of use, making it essential in industries like automotive, construction, and metal fabrication. While it has limitations like outdoor usability and higher initial costs, advancements in technology continue to improve its efficiency and application. Whether you're a beginner or an expert, understanding MIG welding can open doors to numerous opportunities in metalworking.