MIG vs. TIG Welding: Which One is Best for Your Project?
Two of the most common welding methods are MIG (Metal Inert Gas) and TIG (Tungsten Inert Gas) welding.

When it comes to welding, selecting the right process is crucial for ensuring the quality, durability, and efficiency of your project. Two of the most common welding methods are MIG (Metal Inert Gas) and TIG (Tungsten Inert Gas) welding. Both have their advantages and specific applications, but understanding the key differences can help you choose the best one for your needs.
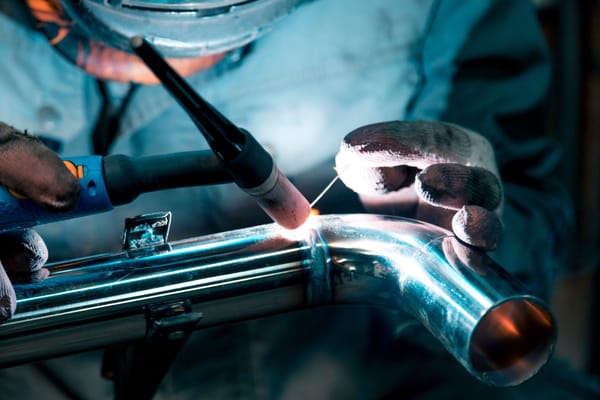
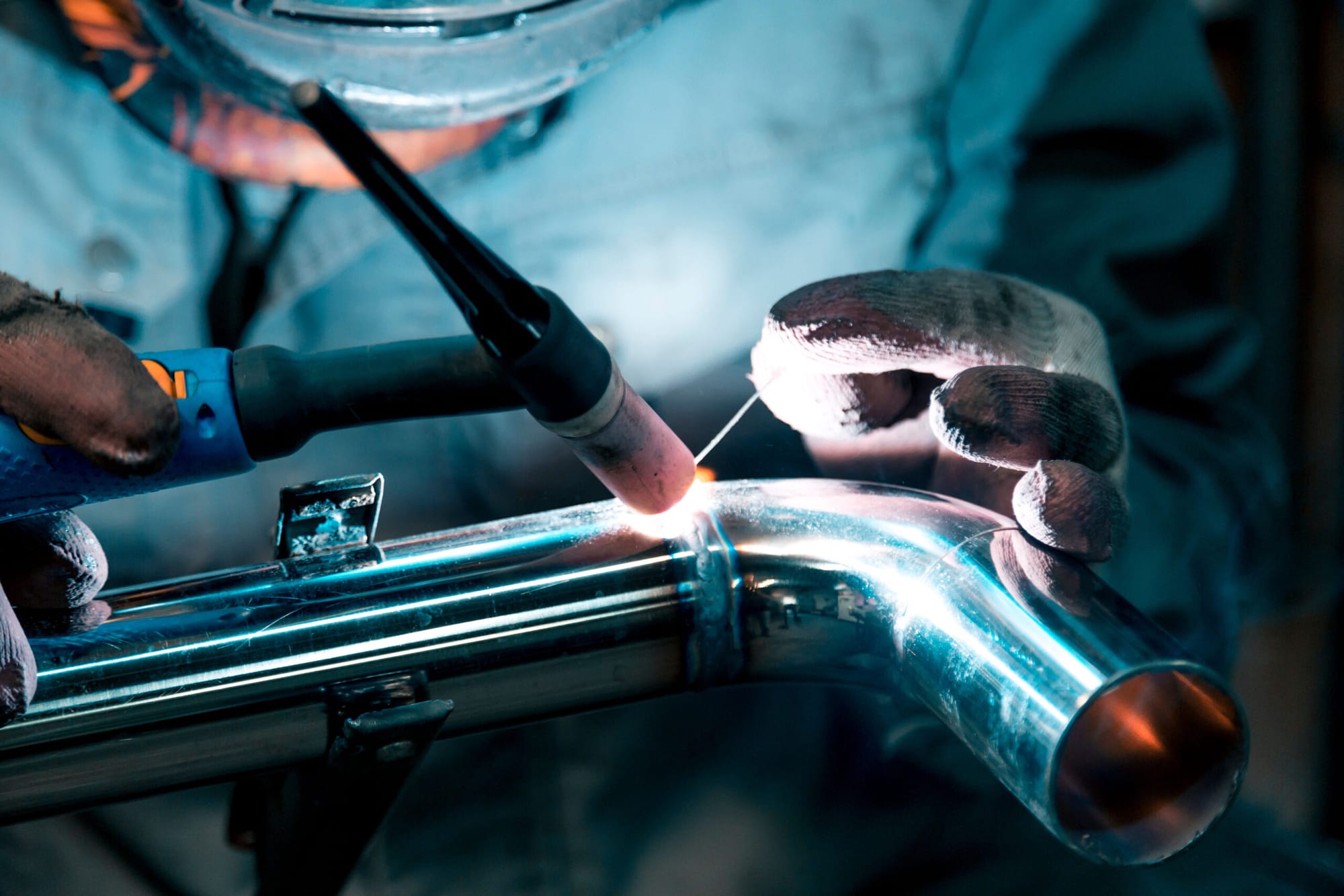
What is MIG Welding?
MIG welding, also known as Gas Metal Arc Welding (GMAW), uses a continuous solid wire electrode fed through a welding gun. The weld area is shielded by an inert gas (usually argon or a mixture of gases) to protect the weld from contamination.

Advantages of MIG Welding:
- Ease of Use: MIG welding is easier to learn, making it ideal for beginners and large-scale production.
- Speed: It allows for faster welding, which is beneficial for projects requiring high productivity.
- Versatility: Suitable for welding a variety of metals, including steel, stainless steel, and aluminum.
- Continuous Welding: The continuous wire feed makes it effective for longer welds.
Ideal Applications:
- Automotive repair
- Construction and fabrication
- Manufacturing industries
- Home and DIY projects
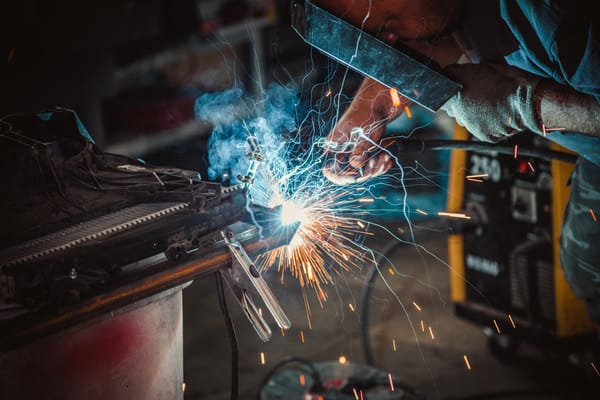
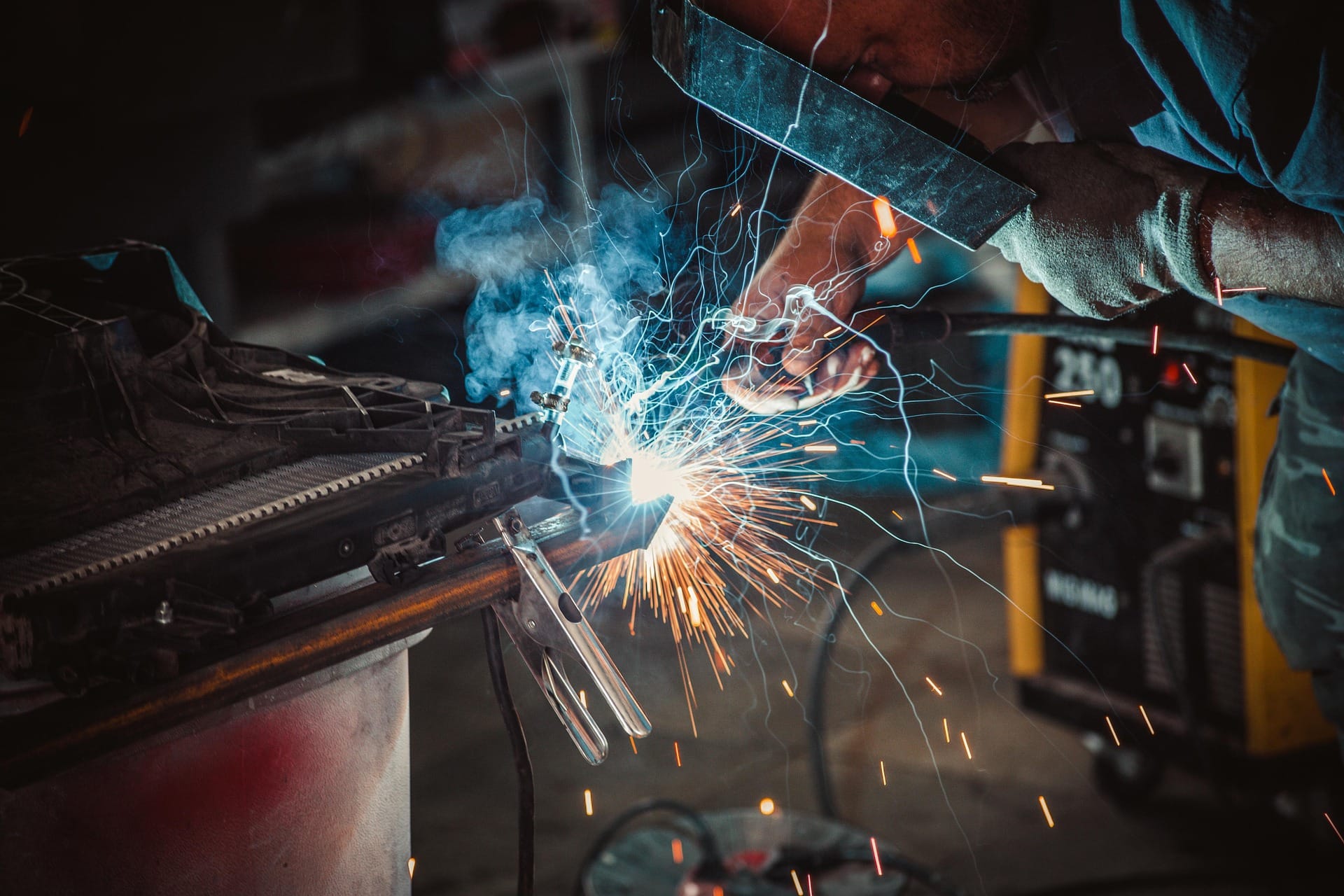
What is TIG Welding?
TIG welding, or Gas Tungsten Arc Welding (GTAW), utilizes a non-consumable tungsten electrode to produce the weld. A filler rod may be used if additional material is needed, and the weld area is protected by an inert gas, usually pure argon.

Advantages of TIG Welding:
- Precision: Offers superior control for detailed and high-quality welds.
- Cleaner Welds: Produces clean, aesthetically pleasing welds with minimal spatter.
- Material Flexibility: Ideal for thin materials and non-ferrous metals like aluminum, magnesium, and copper alloys.
- Strong and Durable: Creates stronger welds due to better penetration and heat control.
Ideal Applications:
- Aerospace and aviation industries
- Art and sculpture
- Custom automotive parts
- Pipe welding
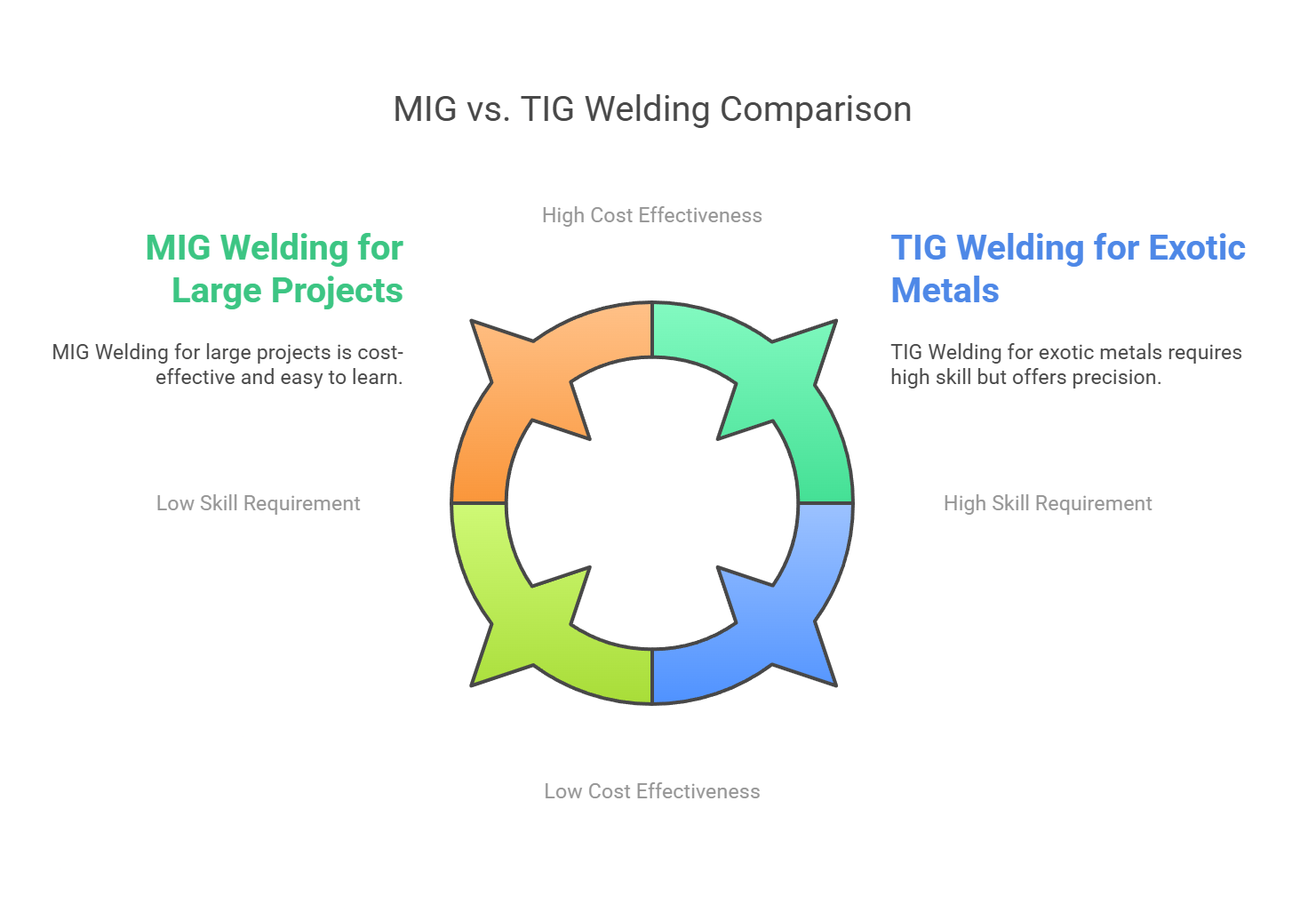
MIG vs. TIG: Key Differences
| Feature | MIG Welding | TIG Welding |
|---|---|---|
| Ease of Use | Easier to learn and use | Requires more skill and precision |
| Speed | Faster for large projects | Slower, more precise process |
| Material Type | Thicker metals, mild steel | Thin metals, aluminum, exotic metals |
| Weld Quality | Functional but less refined | High-quality, clean finishes |
| Cost | More cost-effective for large projects | Higher cost due to slower process |
Which One Should You Choose?
Choosing between MIG and TIG welding depends on your project requirements:
- For beginners or large-scale projects: MIG welding is the better choice due to its ease of use and faster production rate.
- For precision work or thin materials: TIG welding offers better control and cleaner welds, making it ideal for artistic or intricate tasks.
- For budget-conscious projects: MIG welding generally costs less due to faster operation and cheaper equipment.
- For high-strength, high-quality finishes: TIG welding is preferred for critical applications where weld quality is paramount.
Conclusion
Both MIG and TIG welding have unique advantages and applications. By understanding the strengths and limitations of each method, you can select the process that best aligns with your project's goals. Whether you need speed and efficiency or precision and quality, choosing the right welding technique ensures the success and durability of your work.